Tongue Fungal Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Manage Them Safely at Home
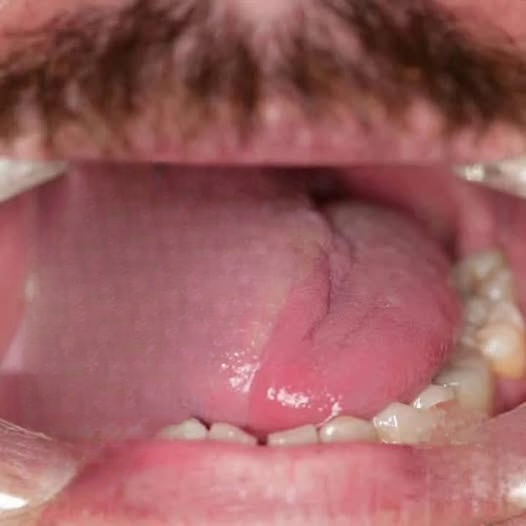
Fungal infections of the tongue are more common than many people realize, especially those caused by an overgrowth of the Candida species—a type of yeast naturally present in the human body. While Candida is typically harmless in small amounts, certain conditions can trigger an imbalance, leading to rapid growth and noticeable symptoms in the mouth, particularly on the tongue.
What Causes Fungal Infections of the Tongue?
There are several underlying factors that can contribute to the development of a tongue-based fungal infection. Some of the most common include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Infrequent or improper brushing and flossing can create an environment where harmful microorganisms thrive. Without regular cleaning, natural oral flora can be disrupted, giving Candida a chance to multiply.
- Antibiotic Use: Taking antibiotics—especially over a long period—can alter the body’s natural microbial balance. Antibiotics don’t just kill harmful bacteria; they may also eliminate beneficial ones, reducing the body’s defense against fungal overgrowth.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, managing chronic illnesses, or living with autoimmune conditions, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Dry Mouth or Dehydration: A lack of sufficient saliva reduces the mouth’s ability to cleanse itself, creating conditions where Candida can flourish.
- Diet High in Sugar or Refined Carbs: Excess sugar in the diet can fuel yeast growth, especially in people already at risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms: What to Look For
Fungal infections of the tongue can present in various ways, and understanding these symptoms can help with early detection and effective treatment.
1. Red, Smooth, and Glossy Tongue
In some cases, the tongue may appear unusually red and shiny. This symptom is often accompanied by a burning or tingling sensation that may worsen when eating spicy, salty, or acidic foods. A red tongue might also be a sign of nutrient deficiencies, such as iron-deficiency anemia, which can occur alongside fungal overgrowth in the mouth.
What Causes Fungal Infections of the Tongue?
There are several underlying factors that can contribute to the development of a tongue-based fungal infection. Some of the most common include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Infrequent or improper brushing and flossing can create an environment where harmful microorganisms thrive. Without regular cleaning, natural oral flora can be disrupted, giving Candida a chance to multiply.
- Antibiotic Use: Taking antibiotics—especially over a long period—can alter the body’s natural microbial balance. Antibiotics don’t just kill harmful bacteria; they may also eliminate beneficial ones, reducing the body’s defense against fungal overgrowth.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, managing chronic illnesses, or living with autoimmune conditions, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Dry Mouth or Dehydration: A lack of sufficient saliva reduces the mouth’s ability to cleanse itself, creating conditions where Candida can flourish.
- Diet High in Sugar or Refined Carbs: Excess sugar in the diet can fuel yeast growth, especially in people already at risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms: What to Look For
Fungal infections of the tongue can present in various ways, and understanding these symptoms can help with early detection and effective treatment.
1. Red, Smooth, and Glossy Tongue
In some cases, the tongue may appear unusually red and shiny. This symptom is often accompanied by a burning or tingling sensation that may worsen when eating spicy, salty, or acidic foods. A red tongue might also be a sign of nutrient deficiencies, such as iron-deficiency anemia, which can occur alongside fungal overgrowth in the mouth.
